MOSFET Introduction :
The MOSFET, commonly known as Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor, is one type of semiconductor device that is widely used in electronic devices to switch and amplify electronic signals.
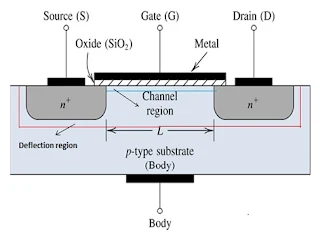
It is an integrated circuit core and can be designed and manufactured in one chip. MOSFET consists of four-terminal devices such as source (S), gate (G), drain (D), body (B).
It is an integrated circuit core and can be designed and manufactured in one chip. MOSFET consists of four-terminal devices such as source (S), gate (G), drain (D), body (B).
History of MOSFET :
1925 - Julius Edgar Lilienfield first established the basic principle of this type of transistor.
1959 - MOSFET was invented on the basis of FET design by Dawon Kahng and Martin Atalla at Bell Labs.
Operation of MOSFET :
MOSFET's goal is to be able to control the voltage and current flow between source and drain. Its work depends upon the MOS capacitor and works almost like a switch. The surface of the semiconductor at the below oxide layer which can be located between the source and drain terminal. It can be inverted from p-type and n-type by applying positive or negative gate voltages. The holes present under the oxide layer with offensive force and holes are pushed downward with the substrate when we apply positive gate voltage. The depletion region is formed, populated by the bound negative charges which are associated with the acceptor atoms and therefore electrons reach the channel. The positive voltage also attracts electrons from the source of n+ and drain regions into the channel. If a voltage is applied between them, the current flows freely between the source and drain, and the electrons in the channel are controlled by the gate. If a negative voltage is applied, a hole channel is formed under the oxide layer instead of a positive voltage.
Types of MOSFET :
- Depletion Mode MOSFET
- Enhancement Mode MOSFET
The channel shows its minimum conductance when there is zero voltage on the gate terminal. Since the voltage on the gate is negative or positive, the channel conductivity will be reduced. This type of transistor is called MOSFET depletion mode.
The channel does not conduct when there is no voltage on the gate terminal. The device has good conductivity when more voltage applied to the gate terminal. This is called a MOSFET enhancement mode.
P-channel MOSFET :
The MOSFET P-channel has a region of the P-channel between drain and source. The MOSFET P-channel consists of negative ions and therefore works with a negative voltage. When the negative voltage is applied to the gate, the electrons present under the oxide layer are pushed downward into the substrate with an excessive force. The depletion region is populated by the bound positive charges which are allied with the donor atoms. The negative voltage attracts holes from p+ source and also drain region into the channel region as well.
N-channel MOSFET :
The MOSFET N-channel has a region of the N-channel between source and drain. When we apply the gate voltage, the holes present in the oxide layer pushed downward with a repulsive force into the substrate. The depletion region is populated by the bound negative charges linked to the acceptor atoms. The positive voltage also attracts electrons from the n+source and drain region. If a voltage is applied between the drain and source, the current flows freely between the source and drain, and the electrons in the channel are controlled by the gate voltage. If a negative voltage is applied a hole channel will be formed under the oxide layer.
MOSFET Application :
- Used as a switch
- Used in MOS integrated circuits
- CMOS circuits
- Switched-mode power supply ( SMPS )
- Inverters
- Used as a constant current source
For detailed information :
Read more >> Applications of MOSFET