As we know that there are available in various forms of 555 timers, single logic gates, microcontrollers, microprocessors, voltage regulators and op-amps like different ICs IC LM741, LM7805, LM35, LM324 IC, LM337, LM338, LM339 IC, LM340, LM1117 and many more ICs are available. Here we have to learn or introduce IC LM358 because it has low power and easy-to-use dual-channel op-amp IC. This IC is designed especially to operate from a single power supply over a wide range of voltages. It is a good, standard operational amplifier and the most important point for this IC is suitable for your needs. LM358 IC is available in a small size as a chip. This IC is most commonly used in the device due to its cost-efficiency. Let us have a deep insight into the introduction, pinout, configuration, features, packages, advantages, and applications of LM358.
LM358 consists of two independent compensated operational amplifiers with high gain frequency. LM 358 IC is available in the cheap sized package so this must be used in real-life applications including DC gain block, conventional OP-AMP circuits design, active filters, and transducer amplifier, This post also gives some information about these ICs like Pinout of LM358, features, Applications, advantages, Pin configuration of LM358, Also give some real-life applications of LM358. So you have to learn some different ideas related to your project you are in the right place to study.
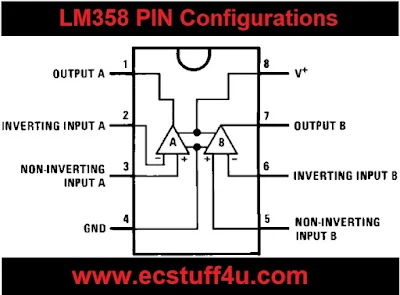
Pinout LM358 :
- LM 358 has eight (8) pins in total having different individual functions associated with each of them.
- Pin-1 and pin-8 are the output of the comparator.
- Pin-2 and pin-6 are inverting inputs.
- Pin-3 and pin-5 are non-inverting inputs.
- Pin-4 is the GND terminal.
- Pin-8 is VCC+.
LM358 pin configurations :
- Here I have to represent with a complete pin diagram along with full animations.
- A properly labelled pin diagram of any device results in better standing of the user, so the users can easily understand pin configurations.
- The complete pinout diagram along with animation, a real image of LM358 and symbolic representation is shown in the figure below.
Features of LM358 IC :
- It consists of 2 OP-AMP internally.
- The output voltage swing is high.
- The large DC voltage gain is around 100 dB.
- Wider bandwidth in 1 MHz(Temperature compensated).
- The supply current drain is very low.
- Wider power supply, in the single power supply, is 3V to 32 V while the dual power supply is +or-1.5 V to +or- 16 V.
- 2mV low input offset voltage.
- Common mode input voltage range comprises ground.
- The differential input voltage range is similar to the power supply voltage.
- Internally frequency compensated for unity gain.
- Short circuit protected outputs.
- Soldering pin temperatures at 260 C.
- The available packages are TO-99, SOIC, DSBGA, and CDIP.
The available package is TO-CAN, SOT-23(5), DSBGA, PDIP. all of these packages along with their dimensions and part numbers are given below:
PACKAGES:
PDIP(8) - 9.81 𝝬 6.35 and unit - mm
DSBGA(8) - 1.31 𝝬 1.31 and unit - mm
TO-CAN(8) - 9.08 𝝬 9.09 and unit - mm
SOIC(8) - 4.90 𝝬 3.91 and unit - mm
Advantages of the LM358 IC :
- Two operational amplifiers are compensated internally.
- Permits direct sensing close to GND and VOUT.
- Well suited with all methods of logic.
- Power drains are appropriate for the operation of the battery.
- Two internally compensated for OP-AMP.
- Eliminates the need for dual supplies.
LM358 has a wide range of real-life applications, we have represented the major applications of LM358 listed below:
- It must be used in the DC gain block.
- It can be used for signal conditioning.
- It is used for active filters.
- Current loop transmitter for 4 to 20mA.
- It can be also used in transducer amplifiers in real-life applications.
- This IC also be used in operational circuits.
- It must be used in real-life applications like shock alarm circuits and dark sensor circuits.
Simple Schock alarm circuit using LM358 :
- The shock alarm circuit using LM358 is very easy to design and it has many applications from home automobiles.
- The main application of this circuit is as an anti-theft alarm in automobiles. In this circuit, a piezoelectric sensor is used as a shock sensor that has to be mounted on the door which you have to guard.
- Here shown in figure LM358 is connected in the inverting Schmitt trigger. The port R1 sets the threshold voltage of the circuit. R1 is used as the feedback resistor.
- When the piezoelectric sensor has not activated the output from the piezoelectric sensor will be low and so will the output of the IC, So at a time output of the sensor is high and activates as a Schmitt trigger. Then it gives the buzzer sound.
- The buzzer remains beeping for some time even if the vibration is detached. This is because when inverting input has little effect when the LM358 IC is triggered and the state can't be easily inverted. So fix the sensor firmly to the surface, wherever you place it and it is always good to place the sensor near to the doorknob.
- So here this figure has to use the 3-volt battery as a power supply and regulate the R2 register to obtain the necessary sensitivity.

Conclusions :
Here this post gives the all about information IC LM 358 like pinout, pin configurations, applications, advantages, features, and also real-life applications. We hope you all understand this topic. Furthermore, for queries regarding your project please give your feedback by commenting in the comment sections.